
- #FREE SSH CLIENT MAC OS X HOW TO#
- #FREE SSH CLIENT MAC OS X MAC OS X#
- #FREE SSH CLIENT MAC OS X GENERATOR#
- #FREE SSH CLIENT MAC OS X ARCHIVE#
- #FREE SSH CLIENT MAC OS X PASSWORD#
Your SSH client might ask you to confirm the server’s host key and add it to the cache before connecting. pem), and SERVER-IP with the public IP address or hostname of your server. $ chmod 600 KEYFILEĬonnect to the server using the following command: $ ssh -i KEYFILE to replace KEYFILE in the previous commands with the path to your private key file (.
#FREE SSH CLIENT MAC OS X HOW TO#
Refer to the FAQ to learn how to obtain your SSH credentials. pem) to 600 using a command like the one below. Set the permissions for your private key file (.
#FREE SSH CLIENT MAC OS X MAC OS X#
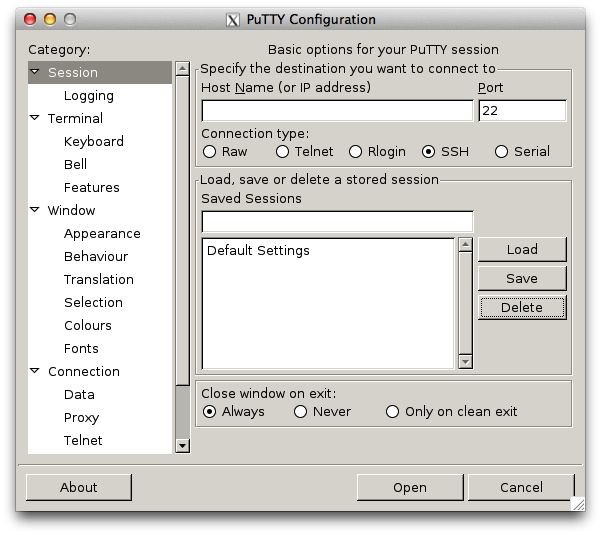
Open a new terminal window on your local system (for example, using “Finder -> Applications -> Utilities -> Terminal” in Mac OS X or the Dash in Ubuntu). In order to log in to your server, follow the steps below: Linux and Mac OS X come bundled with SSH clients by default. TIP: In case of difficulties using PuTTY, refer to the official documentation for troubleshooting advice and resolution for common error messages.Ĭonnect with an SSH client on Linux and Mac OS X using an SSH key You should now be logged in to your server. Go ahead and click “Yes” to this request ( learn more). PuTTY will first ask you to confirm the server’s host key and add it to the cache. Select the session you want to start (in case that you have saved more than one session) and click the “Open” button to open an SSH session to the server. In the “Session” section, click on the “Save” button to save the current configuration. In the “Connection -> Data” section, enter the username bitnami into the “Auto-login username” field, under the “Login details” section. ppk) you’ve previously obtained in the step above. In the “Connection -> SSH -> Auth” section, browse to the private key file (. Refer to the FAQ to learn how to obtain your SSH credentials for your client. Obtain your SSH credentials in order to allow the authentication against the server. Then, click “Save” to save the new session so you can reuse it later. In the PuTTY configuration window, enter the host name or public IP address of your server into the “Host Name (or IP address)” field, as well as into the “Saved Sessions” field. ppk key file format.ĭouble-click the putty.exe file to bring up the PuTTY configuration window. Once the private key has been imported, click the “Save private key” button to convert and save the key in PuTTY’s.

#FREE SSH CLIENT MAC OS X GENERATOR#
Launch the PuTTY Key Generator by double-clicking the puttygen.exe file in the PuTTY installation directory.Ĭlick the “Load” button and select the private key file in. ppk format, you may skip this step.įollow the steps below to convert your. ppk format before you can use it with PuTTY. pem format, it is necessary to convert it to PuTTY’s own. Step 2: Convert your PEM private key to PPK format (optional)
#FREE SSH CLIENT MAC OS X ARCHIVE#
Download the PuTTY ZIP archive from its website.To access the server via SSH tunnel using PuTTY on a specific port using an SSH tunnel, you need to have it configured in order to allow connections to your server. In the instructions below we have selected PuTTY, a free SSH client for Windows and UNIX platforms. In order to access your server via SSH tunnel you need an SSH client. Connect with an SSH client on Windows using an SSH key
#FREE SSH CLIENT MAC OS X PASSWORD#
If you have configured password authentication, you must have the password for the bitnami user account instead of the private key. NOTE: When connecting with an SSH client, you must have the server’s IP address and the SSH private key for the bitnami user account in. If you prefer to use password authentication, follow these instructions to configure the SSH server to support password authentication. IMPORTANT: Before following the steps below, ensure that you have enabled the SSH server (disabled by default) and that your application server is running.īy default, you can log in to the virtual machine over SSH using key-based authentication. Modify the available memory for the virtual machine.Auto-configure a Let's Encrypt certificate.Connect to the virtual machine from another host.Configure the application's IP address or hostname.Learn about the Bitnami Configuration Tool.Configure third-party SMTP for outbound emails.Modify the default login password for the virtual machine.Understand what data Bitnami collects from deployed Bitnami stacks.Learn about Bitnami PHP application modules deprecation.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
